Video Tutorial
I highly recommended watching this tutorial since it is much easy to follow along.
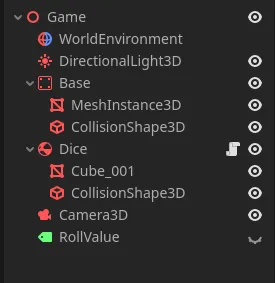
Tree Structure
This is the node tree strcuture that we need in this tutorial.
I have scaled down dice mesh to 0.1 to make it look realastic. If you want same behaviour with different dice, you have to play with gravity and torque force.
Scripting
Attach a script to Dice node and call it dice.gd, open it and lets start coding.
We will start by defining some variables or signals, which we can emit on specific cases
extends RigidBody3D
# This value will be used to reset global_position
@onready var initial_position: Vector3 = global_position;
# A reference to label node which shows the dice outcome
@export var roll_value: Label;
# A flag to track if dice is rolling or not
var is_rolling: bool = false;
func _ready() -> void:
randomize()
Lets define roll method.
func roll() -> void:
roll_value.hide()
is_rolling = true;
sleeping = false;
# Reset to initital
global_position = initial_position;
linear_velocity = Vector3.ZERO
linear_velocity = Vector3.ZERO
# Randomize dice rotation
rotation_degress = Vector3(
randi_range(1, 360),
randi_range(1, 360),
randi_range(1, 360),
)
# Add rotational force to the dice at once
apply_torque_impulse(Vector3.ONE * 0.08)
Lets make input handler and add other logic.
if Input.is_action_just_pressed("ui_accept"):
roll()
# Sleeping is a RigidBody3D property which we
# can use to detect whether our rigidbody is at rest or in motion.
# When our dice is sleeping and is_rolling is true,
# we can say that our dice just stopped moving,
# so it's time to compute roll_value and update the label
if sleeping and is_rolling:
is_rolling = false;
roll_value.show()
roll_value.text = "You Rolled: %s" % get_roll_value()
# Instead of this we can also emit a signal, something like
# dice_rolled.emit(get_roll_value())
Logic to get top face value.
func get_roll_value() -> int:
# we are trying to find which dice face is upward side, but you can change this value to detect any side of dice.
var world_up = Vector3.UP
var threshold = 0.9;
var max_dot = -1;
var sides = {
transform.basis.y: 1, # Top
-transform.basis.y: 6, # Bottom
transform.basis.x: 5, # Right
-transform.basis.x: 2, # Left
transform.basis.z: 3, # Screen Side (You)
-transform.basis.z: 4, # Backwards
}
var value = -1;
for side in sides:
var dot_product = world_up.dot(side.normalized())
# If dot_product of current side is greator than threshold and greator than max_dot
# we will assume that's our favorable value.
if dot_product > threshold and dot_product > max_dot:
max_dot = dot_product
value = sides[side]
return value


